Everything You Need To Know About The New EU AI Act (In 8 Minutes Or Less)
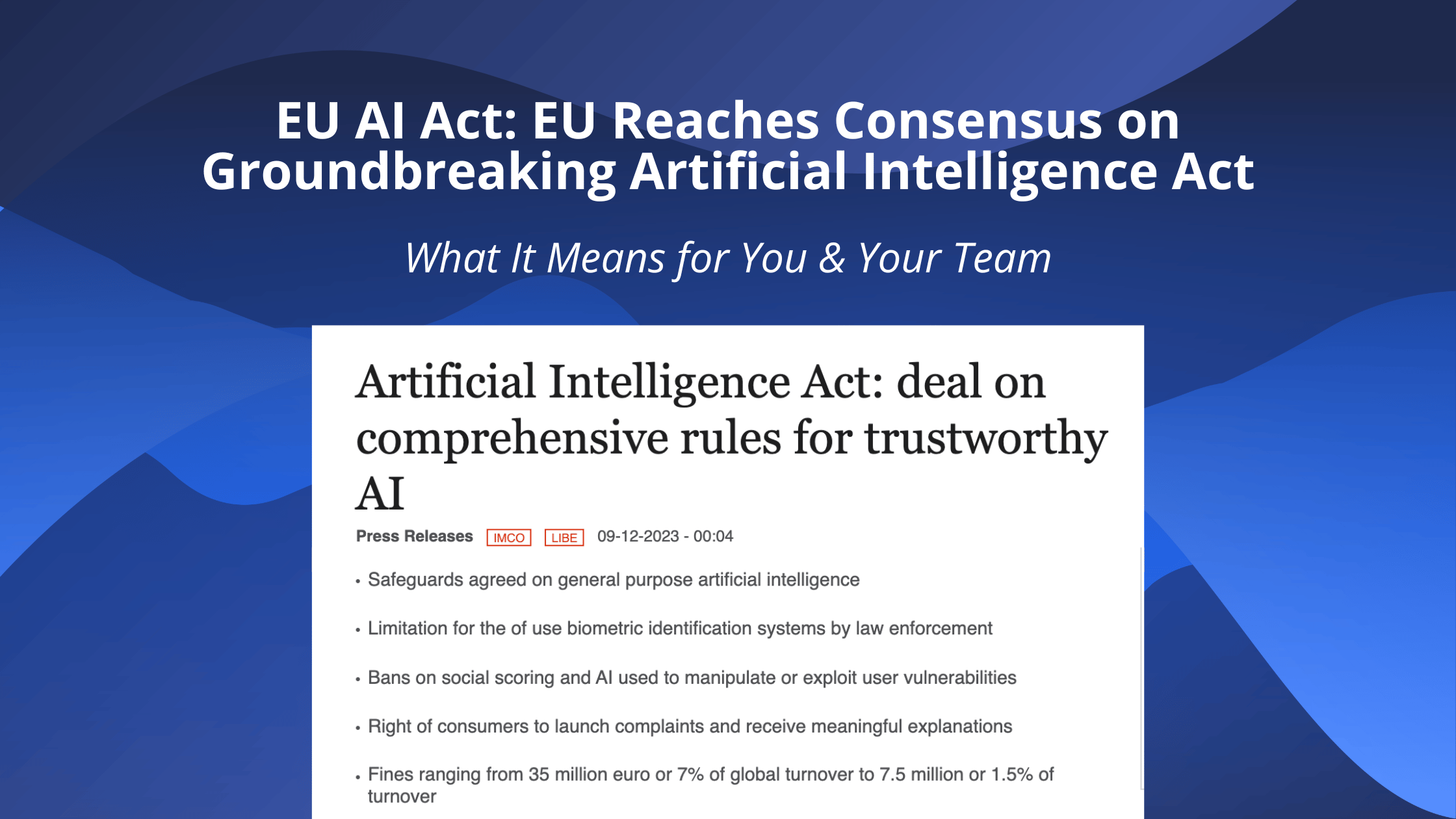
- The European Union has provisionally agreed on the first comprehensive AI laws, after 36 hours of negotiations.
- The European Parliament will vote on these proposals next year. This legislation includes safeguards for AI use within the EU and constraints for law enforcement.
- The AI Act is seen as a historic step by EU officials to promote trustworthy AI development while protecting safety and rights.
- The Act imposes fines for violations and sets a global standard, reflecting the EU’s role in tech regulation. The Act also influences AI companies and governments worldwide, balancing innovation and protection.
So what does this mean for you? We broke down the most important takeaways for the corporate world.
The Top 5 Implications For Companies
1. Prepare for Enhanced Scrutiny on High-Risk Applications
The new legislation puts a strong emphasis on managing the risks associated with AI, particularly in “high-risk areas.” The EU enumerates eight high-risk areas:
- Critical infrastructure that could put citizen’s health and life at risk
- Access to educational and vocational training
- Safety components of products such as medical devices
- Employment, access to self-employment, and worker management
- Essential private and public services, including insurance, access to benefits, and credit scoring
- Law enforcement
- Migration, asylum, and border control
- Administration of justice and democratic processes
Companies in these sectors, or those whose operations intersect with these areas, must ensure their AI systems comply with the heightened regulatory standards. These requirements cover the identification and mitigation of risks, ensuring data quality, sufficient logging of model activity, humans kept in the loop, clear user information and the ability for affected users to file complaints and request explanations of a high-risk application.
Takeaway: Companies should be able to catalog and sort all models by risk level.
2. Expect Significant Fines for Non-Compliance
The Act introduces stringent compliance requirements, and non-compliance can result in substantial financial penalties, with fines going up to 7% of global sales.
Given that Meta was subject to a €1.2 billion fine for GDPR non-compliance in 2023, companies should expect the EU to follow through on enforcement.
This underscores the need for companies to conduct thorough reviews and possibly revamp their AI-driven processes and products. It’s essential for businesses to fully understand and integrate these regulatory requirements into their operations to avoid costly penalties and to align with the new legal framework.
Takeaway: Companies should be able to identify which regulatory framework(s) apply to each model.
3. Brace for Additional Transparency Obligations in 2024 and Beyond
The AI Act intertwines with data protection laws like GDPR. Companies must ensure their AI systems comply with data privacy regulations, especially when handling personal or sensitive data.
Companies employing significant AI technologies, especially those similar to ChatGPT, will be subject to new transparency rules. This includes an obligation to clearly indicate when content, such as deepfakes or other AI-generated materials, is not produced by humans.
High-risk applications must be able to provide model explanations to citizens whose rights are at stake. Additionally, generative AI systems are subject to copyright law and must disclose summaries of the use of copyrighted material in model training.
Takeaway: Companies should track data lineage and consider their transparency policy and human accountability framework.
4. Know That Leading Organizations Are Laying the Groundwork for Ethical AI Audits Already
Businesses must consider the ethical implications of AI use, ensuring that AI systems do not perpetuate biases or discrimination. This includes regular audits of AI algorithms for fairness and bias.
Takeaway: Companies should be prepared to run bias audits on all applicable models. Automated audits are ideal.
5. Teams Should Plan For Additional Skills, Training, and Technical Investments Now
Companies may need to invest in upskilling their workforce to understand and manage AI technologies effectively, ensuring teams are equipped to handle the complexities of AI systems and compliance requirements.
Takeaway: Companies should begin to evaluate AI Governance software and AI trust, risk, security management (AI TRiSM) tools to assist in managing AI across the entire organization. Additionally, teams may need to fill gaps within their teams with additional risk management resources.
Our Take
We enthusiastically welcome the EU’s new AI regulations. This legislation not only validates the importance of AI governance but also opens up new avenues for us to assist businesses in navigating these complex regulations, fostering a safer and more accountable AI landscape.
Are you wondering how this order and related regulations will impact your business? Let us know a little more about your organization and how we can help maximize your AI while minimizing your risk.
Be Ready for the EU AI Act
Is reading hundreds of pages of upcoming legislation not really your thing? Good news! It’s ours! Enter your email to stay informed and on track in real-time.